Before choosing a heater, you need to calculate the minimum heating output required for your specific space.
Usually for approximate calculation It is enough to divide the volume of the room in cubic meters by 30. Managers usually use this method when advising customers by phone. This calculation allows you to quickly estimate approximately what the total thermal power may be needed to warm up the room.
Therefore, there is no danger that your child will stand in too hot and too cold room. The temperature is always whatever you think is appropriate. We remind you that separate models of convectors are provided for the bathroom and kitchen, taking into account the specific functions of these rooms. Radiation kitchen convectors have fast drying and high moisture resistance. Bathroom convectors are also moisture-proof, allowing the air purifier to be cleaned without the need to remove the unit from the wall.
Choosing an air conditioner is correct and easy if you consider these three factors
Choose an air conditioner or how to make it simple and right choice. from the right air conditioner for you. When choosing an air conditioner, it is important to know the volume of the room you want to condition.
The number one factor when choosing an air conditioner
- What are your expectations from an air conditioner?
- The budget you have.
For example, to select a heat gun for a room (or office) with an area of 50 m² and a ceiling height of 3 m (150 m³), 5.0 kW of thermal power will be required. Our calculation looks like this: 150 / 30 = 5.0
This calculation option is mainly used for calculations additional heating to those rooms where there is already some kind of heating and you just need to warm the air to a comfortable temperature.
To most accurately calculate the required air conditioner power, many factors must be taken into account. Other factors that influence the choice of air conditioner capacity are: insulation from the room, exposure, thickness of walls, floors, insulation in the attic, amount of glazing in the building, type of window frames and the like.
The second important factor when choosing an air conditioner
All these factors are calculated by ours, which will make your room free to view. This is the generalized first factor for choosing an air conditioner. Here the specification of the air conditioner itself is taken into account according to your preferences. By specification we mean maximum noise levels, design, size of air conditioners, etc. It is important to know if you will be using the air conditioner for heating. If the air conditioner is to be used for space heating, it must be a converter that will allow the device to be efficient and economical when low temperatures outside air.
However, this method of calculation is not suitable for unheated premises, and also if it is necessary, in addition to the volume of the room, to take into account the difference in temperatures inside and outside, and design features the building itself (walls, insulation, etc.)
Accurate calculation of the heater's thermal power:
To calculate thermal power taking into account additional conditions premises and temperature conditions, the following formula is used:
Another thing to keep in mind when choosing an air conditioner
This happens because more high prices some brands of air conditioners are guaranteed high quality manufacturing, low energy consumption, long term service, low noise, highly innovative embedded electronics, quality building materials, air purification systems and others. Investing in an air conditioner upper class will pay you for comfort and low electricity bills for a guaranteed long service life.
When the air conditioners are from lower classes, most of the above-mentioned symptoms are absent, resulting in higher electricity bills and short term services. Keep in mind that when choosing an air conditioner, this is quite a significant investment and choosing an inexpensive air conditioner will in no way save you money. This is the most important thing when choosing an air conditioner.
V × ΔT × K = kcal/hour , or
V × ΔT × K / 860 = kW, Where
V— Volume of the heated room in cubic meters;
ΔT— The difference between the air temperatures inside and outside. For example, if the outside air temperature is -5 °C and the required indoor temperature is +18 °C, then the temperature difference is 23 degrees;
What do you need to know when choosing an air conditioner?
However, if you do it yourself, calculate what kind of conditioner you need
Use of modern air conditioning - perfect way cool or warm the room. The climate can save you from the heat in the summer, while at the same time it will remove moisture from the air. When purchasing an air conditioner, it is very important to choose an air conditioner that will suit the needs of your room. Air conditioners are available in various types, such as standard wall mounted air conditioners, but window air conditioners, cooling towers, and many others.K— Thermal insulation coefficient of the room. It depends on the type of construction and insulation of the room.
K=3.0-4.0— Simplified wooden structure or corrugated construction metal sheet. No thermal insulation.
K=2.0-2.9— Simplified building design, single brickwork, simplified window and roof design. Little thermal insulation.
In addition to the different types of air conditioners, they differ in their power. Air conditioner capacity is measured in British thermal units. Accordingly, than bigger room, the more powerful the air conditioner should be. Therefore, there are many things to consider when choosing an air conditioner. Purchasing a much more powerful air conditioner than is required for the room will result in the air conditioner turning off before reaching set temperature in room. In this case, you will not only reduce the comfort of the room, but you will also bad influence on the correct temperature distribution in this room.
K=1.0-1.9— Standard construction, double brickwork, few windows, standard roof. Average thermal insulation.
K=0.6-0.9— Improved building design, brick walls double insulated, few double glazed windows, thick floor base, high quality roof thermal insulation material. High thermal insulation.
If you choose an air conditioner whose power is less than necessary, then it will work too long and will not be able to heat or cool the room. This will not only consume more electricity, but will also shorten its normal lifespan and cause it to break down more often. Moreover, when the air conditioner is less powerful, it will not be able to cool and warm well.
What you need to know about room size when choosing an air conditioner
This assumes your room has standard height 6 meters. The power of the air conditioner, as stated above, is determined by the volume of the room as the main factor and several additional factors, which represent the exposure and density of the room, or are well insulated, and others. First, measure the length of the room for which you are choosing an air conditioner. Then measure the width of the same room. Finally, measure the height of the room from floor to ceiling. Multiply length by width by height.
When choosing the value of the thermal insulation coefficient, you must take into account whether the building is old or new, since old buildings require more heat to warm up (accordingly, the value of the coefficient should be higher).
For our example, if we take into account the temperature difference (for example, 23 °C) and clarify the thermal insulation coefficient (for example, we have an old building with double brickwork, take the value 1.9), then the calculation of the required thermal power of the heater will look like this:
Disadvantages of cast iron products
The final number is the volume of the room. The volume of the room is important when choosing an air conditioner. Keep in mind that most air conditioners can cool down a bit before warming up. The resulting room volume number simply needs to account for the air conditioner's output per volume, given that you need 100 watts to heat and cool 80 watts per cubic meter.
How do you calculate the required power?
We will now calculate the volume by multiplying 26 m² by the height of 6 m to get 6 m³, which we can easily consider as 68 cubic meters. Likewise, we can also consider the power required for cooling. We hope you found this helpful when choosing an air conditioner.
150 × 23 × 1.9 / 860 = 7.62
That is, as you can see, the refined calculation showed that to warm up this particular room, a greater thermal heating power will be needed than was calculated using the simplified formula.
This method of calculation is applicable to any type thermal equipment, except perhaps infrared heaters, because the principle of perceived heat is used there. It is suitable for any other types of heaters - water, electric, gas and liquid fuel.
Calculation of air conditioner power. The calculation of the power of air conditioners used for heating is the same as for any other heating method - central heating, natural gas, electricity, wood, etc. if the air conditioner is used only in cooling mode, and in transition seasons the calculations are the same. The differences between heating and cooling modes lie in the temperature difference between the outside and inside air.
The main feature of using air conditioners for heating is that their power gradually decreases as the temperature difference between the outside and inside air increases, which is not available in any other way for heating.
After calculating the required thermal power, you can begin to select the type and model of the heater.
How to determine heating power
If you have built own house and are ready to begin construction utility networks, you need to familiarize yourself with some nuances that will affect the correctness of the installation work. Let's talk about the heating system. Let's start with the premises.
In this case I have an idea that we have a pool that is filled with water from a pipe and drained from 5 - it asks in which case the pool will be constantly filled. The pool problem is not chosen at random, because in the case of under the inlet pipe, it means that the air conditioner is running in the room and less than 5 outgoing - at least five ways to lose heat from your home, which are as follows.
- Window losses Local losses from external walls.
- Disadvantages from adjacent internal walls.
- Excerpts from the rooms above your premises.
- Introducing losses is unsealed holes in the room.
It would seem that you can count on this - buy a boiler, pipes and radiators, install and connect it all. But it's not that simple. After all, you will have to invest your own money. A properly calculated system will save a lot of money.
Heating boiler calculation
This is the simplest of calculations because the power heating boiler depends on the area of the premises that it will heat. To do this, take the ratio - 1 kilowatt of thermal energy heats 10 square meters area with a ceiling height of no higher than 3 meters. Take the total area of the house, divide by 10 and get the power of the heating boiler.
Accurate calculation of the heater's thermal power
In short, this is due to the fact that the partial pressure of water is higher, which causes it to be warm and wet air rises to the ceiling, and cold and dry air falls to the floor. This phenomenon is called convection, and as a final effect you have ten times more losses for the ceiling than on the floor.
Thermal losses in a room are the sum of losses from individual surfaces. The heat loss of each surface is measured as a factor that indicates how much energy passes through one square meter of that surface. Each material or structure, such as its joinery, has its own coefficient.
This simplified formula can only be used for single-circuit devices. For a double-circuit unit, the calculation will have to be done differently. For example, a house with an area of 240 square meters cannot be heated wall-mounted boiler with a power of 24 kilowatts. One heating circuit will work to heat the premises, and the second will work to heat water for household needs. Therefore, the power will have to be divided by 2, and it turns out that such a boiler can heat a house with an area of no more than 120 square meters.
Approximate heat transfer coefficients for glass panels are given in the following table. It's much better in summer infrared rays passed freely through window frames. The resulting value should be multiplied by the actual window area to find out how much you are spending on it. A very damn idea: if you decide to heat yourself with air conditioning, think about the carpentry first, as this will reduce the power of your required air conditioning unit, and the money you save on a smaller machine will cover part of the investment for the window frames.
With a single-circuit device everything is much simpler, but even here a small backlog is needed. For example, by choosing a single-circuit boiler with a capacity of 24 kilowatts, you can guarantee that it will easily heat a house with an area of 200 square meters with a ceiling height of 2.5-2.6 meters. If the ceilings in the house are 3 meters, then the device will be able to heat the rooms with total area 170 squares. These are the manipulations.
In fact, this rule applies not only to heating air conditioners. Calculating the power of air conditioners for heating is a very serious topic that should be completed with a calculator. The author of this site is a software engineer, but will require more in-depth knowledge of the processes that occur during temperature transfer.
First you need to determine the power of the air conditioner. To do this, it is necessary to take into account all temperatures entering the room. The air conditioner power should be equal to or slightly greater than the obtained heat loss compensation value. Thermal loads due to external conditions.
Calculation of heating radiators in an apartment is also very important. And here you will first have to determine their number, and for each room separately. To do this, you need to take as a basis not area, but cubic capacity. If there are few batteries, this will ensure a lack of heat, which means the rooms will always be cold. If there are too many radiators, then you will have to pay more for such heat by purchasing large quantity fuel. So everything should be in moderation.
Heat loss due to temperature differences outside the building through walls, ceilings, floors, windows and doors. Temperature difference between outside and internal part buildings during the summer is positive as a result of heat flow. Warmth from sunlight through the glazed area.
External air ventilation and penetration into rooms create additional heat loss. Heat loads due to internal sources. Heat generated by people. The heat generated by lamps and lamps Appliances- stoves, refrigerators, TVs, computers, etc. As well as industrial and other facilities.
Alternative connection of heating radiators in an autonomous system
For example, let's take a room with an area of 10 square meters with a ceiling height of 3 meters. There is a standard indicator that determines the amount of thermal energy that is enough to heat 1 cubic meter of space. It is equal to 39-41 watts. To calculate the volume of a room, you need to multiply the area by the height of the room - in our example it is 30 cubic meters. Now we multiply this value by 41 watts. The result is 1230 watts. This is the power that will pull the volume of a given room.
Formula for calculating air conditioner power by type. Select the type of air conditioner and its location. After calculating the required power, you must provide a description of each type of air conditioner, its pros and cons can be found. MOBILE AIR CONDITIONER is suitable for those who often change their place of residence. Keep in mind that the mobile air conditioner is not very small in size and weight, it is noticeably louder and more consuming than. Hot air released and unloaded from the air conditioner through corrugated hose through open window or hole for walls.
This disadvantage of mobile air conditioners limits both the efficiency and portability of this device. The most common is indoor unit on the wall in the room. They are relatively inexpensive, compact and almost silent. They have a varied range of filters and filters. To install them there is no need for suspended ceiling and a specific place in any room.
There is another standard indicator - this is the amount of thermal energy that 1 radiator section can generate. It is equal to 200 watts. Now we divide the resulting total power by the power of one section -1230/200=6.15. This is the required number of sections that need to be rounded up. The result is the number “7”. This means that in this room you can install a radiator with seven sections. It's that simple.
For corner rooms calculation cast iron batteries carried out using an additional correction factor, which depends on the region. The coefficient is 1.1-1.3. To avoid mistakes, take the maximum indicator as a basis. The formula will be like this - 1230x1.3/200=7.995. Round up to 8.
Attention! In our case, the number of sections is not so large. Sometimes this number goes beyond a couple of dozens. For such cases, the advice is to divide the number of sections into equal amount batteries installed evenly throughout the building and ideally under a window.
Calculation of other heating materials
For those who have never encountered the installation of a heating system, it will be very difficult to calculate necessary materials. The minimum that is needed is to at least have an idea of how the pipes will be laid out, how the heating boiler will be connected, and how the batteries will be connected. Therefore, before you start counting, you need to study the work scheme heating system. If you cannot cope with this, then it is better to contact specialists.
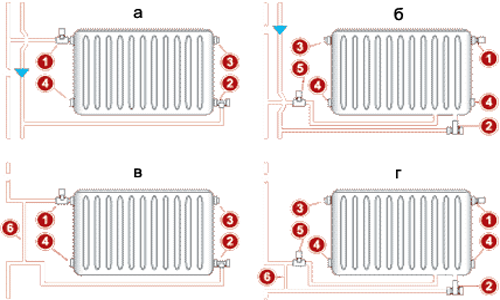
Radiator connection diagrams
What materials are needed for a heating system? Let's look at them using an example double-circuit boiler. To connect it to the home heating system, you will need at least four ball valves with detachable connections - one for each input and output of the two circuits. Each tap has one threaded adapter to connect it to the pipelines. You will definitely need two filters for mechanical cleaning water entering the boiler.
Now let's move on to tying the radiators. Here you need two valves (regulating and shut-off), a Mayevsky valve (for air release), a plug, two threaded adapter and two tees for connecting the pipes to the main line. And this is a kit for only one radiator. To calculate all the necessary products, you will have to multiply this by the number of batteries that are planned in your home.
As for the pipes, you will have to measure the distances from the radiators to the boiler and multiply the resulting footage by two. Because many systems operate on the principle of coolant supply and return. The only problem may arise with the diameters of the pipelines, but not everything is so complicated here. Many systems mainly use pipes from 20 to 32 millimeters in diameter. And if your house is not very large in size, then this figure will be sufficient.
Conclusion on the topic
As you can see, calculating the heating power of a cottage is a serious matter. Here it is necessary to take into account many parameters of the house itself. But in general, these mathematical calculations are not difficult if you understand them.