In private houses there are always several utility rooms or technical premises, where the interior requirements are small. But you still need to heat them, and in order not to waste money on buying modern radiators, you can install a steel register welded from pipes there. And, although everyone has seen such simple heating devices with their own eyes, not everyone knows their structure. This material is to help those homeowners who want to independently manufacture, install and connect heating registers to their system.
Construction of heating registers
Despite the fact that such heaters are considered outdated and not very attractive appearance, they continue to be widely used in the most different areas, For example:
- for heating production premises industrial enterprises;
- as an autonomous heater in garages;
- as a water heating element built inside a brick oven.
Note. Furnace register from smooth pipes heating is calculated and manufactured depending on the power and design of the stove.
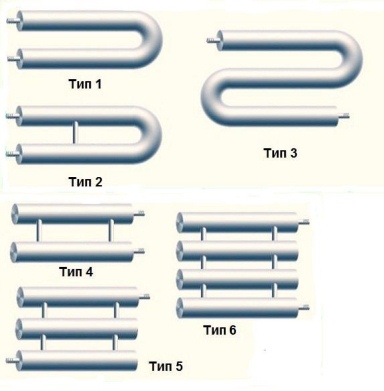
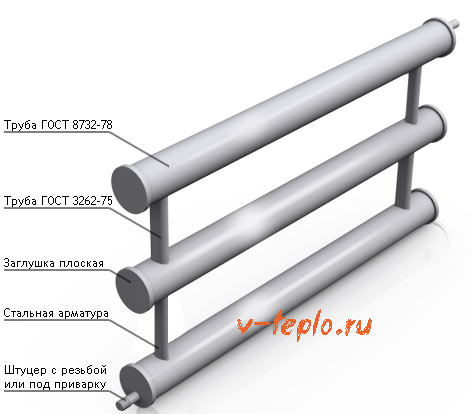
By design, heating devices are divided into 2 types: sectional and in the form of a coil. In the first case, the role of 1 section is played by each horizontal pipe, the flow of coolant through them is ensured by vertical jumpers. They are made from pipes of smaller diameter in order to create artificial resistance to flow and increase heat transfer from each section. The pipes from which the sectional heating register is made are plugged at the ends, and the coolant is supplied according to the “top to bottom” scheme.

The design of the heater in the form of a coil is clear from its name. Here the diameters do not narrow; water flows freely through the entire device, changing direction several times. The heat transfer of this register is lower than that of a sectional one, but the hydraulic resistance is less and it is somewhat simpler to manufacture.

Advice. It is preferable to make sectional heaters for utility rooms or garages, where uniform heating and comfortable air temperature are important. It is better to install coils as standby heaters at the very end of a two-pipe system. They work great there because of their low resistance.

Heating registers from smooth pipes of round and rectangular cross-section are welded. However, the generally accepted design is ordinary round pipes from low carbon steel type St3, St10 and even St0. If the battery is designed to work with steam system, then take steel St20. It is not recommended to make sections with a rectangular cross-section; they are less washed by the convective air flow, which means they will give off less heat. For garage heating, autonomous registers are made, filled with antifreeze or transformer oil, and an electric heating element is built into the lower section from the end.

Advantages and disadvantages
Before you start making heating registers, you need to evaluate all the pros and cons of these heaters, so that your expectations are not disappointed later. So, first about the advantages:
- low cost and ease of manufacture;
- low hydraulic resistance: thanks to this, the heater can be used in the “tail” of any system;
- reliability and durability: the register is qualitatively welded from ordinary pipes, will quietly serve for at least 20 years;
- resistance to pressure drops and water hammer;
- The smooth surface facilitates easy removal of dust when cleaning premises.
Unfortunately, a home-made heating register also has a lot of disadvantages. The main one is low heat transfer with a significant mass of the device. That is, to provide a room of average size comfortable temperature, the register should be of decent size. Let's give a simple example taken from technical literature. If the temperature difference between the coolant and the room is 65 ºС (DT), a register welded from 4 DN32 pipes 1 m long will deliver only 453 W, and from 4 DN100 pipes – 855 W. It turns out that based on the heat transfer per 1 m length, any panel or sectional radiator at least twice as powerful.
Note. The presented data were determined experimentally at a high coolant flow rate of 300 kg/h.
Other negative aspects of smooth-tube registers are not so critical, although significant:
- holds a large volume of water: the disadvantage does not play a big role if there are 1-2 such heating devices for the entire system;
- During operation, it is very difficult to increase or decrease the power of registers made of smooth pipes. You can’t do without dismantling the welding machine;
- are susceptible to corrosion and require periodic maintenance with painting;
- They have an unpresentable appearance: the defect can be corrected; if necessary, the heater is hidden behind a decorative screen.
Having analyzed the advantages and disadvantages of smooth-tube devices, we can conclude that their scope of application in private housing construction is very limited. As already mentioned, registers can be used for heating different rooms with low requirements for comfort and interior.
When selecting materials, you need to decide what pipe diameters to take and what their total length should be. All these parameters are arbitrary; you can make a heater from any pipes, and take its length convenient for placement in the room. But to submit required amount heat, it is necessary to ensure a sufficient heat exchange area. To do this, it is recommended to perform an approximate calculation of the register based on the surface area.
Making such a calculation is quite simple. Need to calculate the area outer surface all sections in m2 and multiply the resulting value by 330 W. Offering this method, we proceed from the statement that 1 m2 of register surface will give off 330 W of heat at a coolant temperature of 60 ºС and room air temperature of 18 ºС.
Advice. You don’t have to do manual calculations, but use a simple EXEL program and then correctly weld the register according to the exact parameters. You can download the program in one click from the link: http://al-vo.ru/wp-content/uploads/2014/02/teplootdacha-registra-otopleniya.xls.

For a person who has welding skills, it will not be difficult to independently weld the register according to the available drawings. It is necessary to prepare and cut pipes into sections and jumpers, cut from steel sheet stubs. The assembly sequence is arbitrary; after welding, the heater should be checked for leaks. When manufacturing and installing registers, consider the following recommendations:
- you should not take pipes with too thin or thick walls: the former will cool faster and last less, and the latter will take a long time to warm up and are difficult to adjust;
- do not forget to build a Mayevsky valve into the end of the upper section for bleeding air;
- when welding coils, the rotating section can be made from two ready-made elbows if it is not possible to use a pipe bender;
- Place a tap at the coolant inlet and a valve at the outlet;
- remember that the registers are installed with an invisible bias towards the connection of the supply pipe. Then Mayevsky's crane will be at the highest point.

Conclusion
Smooth-tube registers cannot be considered a relic of the past, since they are attractive due to their low cost and are still successfully used in various situations. But you should not load the system of a private home with such heating devices; the volume of heated water will then increase many times over, which will have a larger impact on energy consumption.
A register is a heat exchanger with parallel mounted pipes with a diameter of over 32 mm, connected by jumpers from pipes of a smaller diameter. They can also be made in the form of a coil. The devices perform the same functions as radiators, but differ in the ability to manufacture them independently.
As a rule, registers provide heating in warehouses, utility rooms, garages, and some low-rise residential buildings, but can be equipped as part of the interior of ordinary rooms. Heat exchangers are used as elements of one- and two-pipe heating systems with increased fire and sanitary standards.
Register heat exchanger design

The heat exchanger consists of simple details, and welding the register with your own hands if you have welding skills is not difficult. At self-production heating device can be accurately maintained in its required dimensions and technical specifications, necessary for the existing operating conditions. Purchasing a ready-made register can cost approximately 3 times more than the cost of materials for manufacturing the structure.
More often, carbon steel pipes are used to make a heating register. Materials made from stainless low-alloy steel and cast iron are also used. The distance between sections in the register should be 50 mm greater than their diameter. The registers are installed with a slope along the coolant movement of at least 0.05%.
To increase the heat transfer of the device, jumpers are mounted as close as possible to the ends of the horizontal parts. The coolant must flow into top part device, flow through the sections and exit their lower horizontal element.

Pipes in the coil type of registers are connected by arcs of the same diameter. When using an S-shaped heating device, heating efficiency increases by increasing the heat exchange area and reducing hydraulic resistance.
To install heating registers in residential premises, it is recommended to use pipes with a diameter of 3 to 8 cm to match the load on the domestic boiler. When calculating the number of sections and parameters of the workpieces, the heat transfer of the pipe for each of its parts is taken into account. linear meter. For example, 1 m of pipe with internal diameter 60 mm is able to heat about 1 m² of room area.
Design parameters increase by 20-40% with poor thermal insulation of the room and a large number of windows.
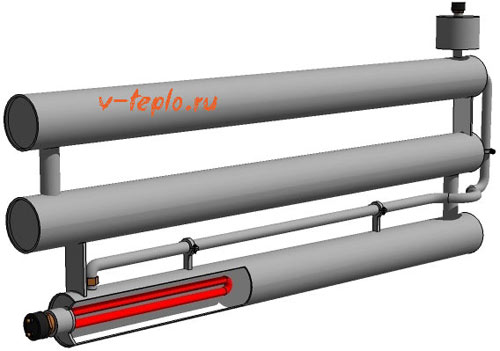
The lower section is located 15-20 cm from the floor surface. For autonomous operation of the register heat exchanger, a heating element with a power of 1.6 to 6 kW is installed in them via a flange connection.
Advantages of using a register

Registered heat exchangers have certain advantages in front of other heating devices:
- Homemade heating registers are different large sizes, therefore, they provide more uniform heat transfer in contrast to radiators, which are local heat sources.
- The devices are easy to clean and do not have hard to reach places where dust accumulates.
- With high-quality welding of parts, heat exchangers can withstand significant pressure and high temperature coolant.
- When the device is equipped with a heating element, it can serve autonomous source heating.
- A well-installed heating register can last at least 25 years without repair.
At the same time, the heating registers have worst characteristics in comparison with radiators of the same size, in which the heat exchange surface is formed more compactly. Maximum operating pressure coolant medium for which a register heat exchanger can be designed is 10 kgf/cm². The system works more efficiently with the installation of a circulation pump.
Preparation of material and welding of parts
To install heating devices in the form of registers, it is necessary to prepare pipe and consumables:
- smooth steel pipes diameter from 76 to 159 mm;
- pipes with a diameter of 32 mm for jumpers;
- inlet and outlet pipes for welding, threaded or flange type diameter from 35 mm;
- threaded fitting for connecting an air vent (Mayevsky valve);
- plugs for pipe diameters;
- floor supports made from corners or brackets for mounting to the wall.
For the manufacture of such heat exchangers, pipes with diameters of 76, 89, 108 and 159 mm are most often used. Products with profile, rectangular or square sections are also used.
Tools you will need:
- welding machine;
- gas key;
- grinder (grinder);
- hammer, electrodes;
- roulette, level;
- welder protective equipment.
![]()
The joining surfaces of the parts are cleaned and degreased before welding to avoid defects in the seams. The ends of the pipes must be perpendicular to their axes. Pipe processing large diameter produced on milling machines or gas-acid cutting.
The pipes are cut into pieces of calculated sizes, the ends are cleaned with a grinder. On horizontal pipes ah, the holes for the jumpers are marked and cut, the pipes must fit into the hole.
Jumpers inserted into the holes are welded to horizontally laid pipes in accordance with the dimensions. Plugs are welded to the ends of the register elements. The inlet and outlet pipes are welded into pre-cut holes at two ends (diagonally).
At one of the upper ends a threaded pipe is welded for installing a Mayevsky tap. All seams are cleaned with a sander to give an aesthetic appearance. Racks are welded to the structure (if the device is installed on the floor).
To check the register for leaks, the lower outlet for the coolant outlet is closed with a plug. The structure is filled with water and inspected for leaks. When they are detected, the water is drained and the problem areas are boiled again. The seams are cleaned again and the register is painted.
Heating devices are the basis of any heating system. In industrial, production and warehouses Heating registers have long been used - installations that represent smooth-walled pipes welded together. IN Lately they are in wide demand among private owners. The registers contain significantly more coolant inside them than in classic radiators, thanks to which they radiate heat longer.
Main classification
The registers offered by the market can be divided into two types:
- Coil (S-shaped)
- Sectional
Coil (S-shaped)
Coil registers consisting of several sections have become widespread. The latter are connected to each other by arcs whose diameter is comparable to the sectional one. The result is a pipe of a continuous configuration, for which the entire surface is working. The efficiency of the installations is very high.
For the manufacture of coil registers, a smooth-walled steel pipe with a high carbon content is used. The areas where narrowing occurs are eliminated, due to which the hydraulic resistance inside is significantly reduced. There are also models on the market made of low-alloy or of stainless steel, cast iron.
Sectional
The most popular among private owners are sectional heating registers, consisting of pipes closed with plugs and connected to each other. The coolant is passed through the upper pipe, at the end of which it flows into the next one - and so on until the exit.
To increase the heat transfer coefficient, the transition for the coolant between the pipes is made as close to the edge as possible. Plugs between pipes come in one of two types: elliptical or flat. The inlet pipe is made to be flanged, threaded or welded.
Sectional heating registers are equipped with a threaded fitting, through which a drain for accumulated waste is mounted. air masses. The diameter of the main horizontal pipes is different and varies from 25 mm to 40 cm (in devices household use– up to 16 cm). The transition is carried out using pipes of a smaller cross-section. Another feature of the installations is that the maximum pressure inside should not exceed 1 MPa.
Subtypes heating registers
In addition to their own configuration, heating registers can be divided into subtypes according to the following criteria:
- Location options
- Material of manufacture
Location options
Depending on the location of the heating registers, they are divided into two categories:
- Portable (with heating element)
- Stationary

Portable or mobile devices does not require reference to a specific location and, as a rule, operates from electrical network 220 V. Inside there are heating elements with a power of 1.6 to 6 kW, which heat the coolant. Similar devices are used in garages, construction sites, cottages, etc.
Stationary registers are located in a specific place, as if heating radiators, and require connection to the boiler. The latter will heat the coolant and force it to circulate through the heating device.
Material of manufacture
Depending on the material of manufacture, heating registers are of the following types:
- Steel
- Aluminum
- Cast iron
Steel registers are the most common. They are connected to the heating system using threaded connections or welding. The products are characterized by a high heat transfer coefficient and reasonable cost.

Small specific gravity aluminum registers, corrosion resistance, no seams and high performance heat transfer has determined the demand for such products among buyers. They are made by monolithic casting. A significant disadvantage is the high cost.
Cast iron radiators are connected to the heating system via a monolithic flange connection. Reasonable cost and simple installation are the main advantages of the products. However, they are less inert than their analogues and therefore take longer to heat up.
How to count the number of ribs
Before purchasing a heating register, you must Special attention refer to the pipe diameter. Experts recommend choosing installations for your home with a diameter of 3-4 cm, but not more than 8 cm. The main reason for this decision is that a household heating boiler is not able to produce the amount of heat that would be enough to properly heat large surfaces.

Read also about heating radiators
When making calculations, you should take into account the length of one register rib and the heat transfer per each meter. For example, a product 1 m long with an internal cross-section of 6 cm allows you to heat about 1 square.
Having counted the required number of edges, rounding is done upward. Under certain conditions, the obtained value can be increased by 20-50%. These include:
- A large number of window openings, indoor doors
- Small wall thickness
- Poor insulation of premises
How to install a heating register
Every owner can install a heating register without involving a specialist in the work. To simplify assembly operations, it is first necessary to prepare each element of the heating system according to the project.

One of the main requirements is a high-quality connection of the register with pipelines. It must withstand maximum permissible load– 10 MPa. If the joining is done by welding, you need to monitor the quality of the seams.
Heating registers must be located closer to the floor surface. The larger the diameter of the main pipe, the less resistance there will be for the circulating coolant.

The effectiveness of the device depends on large number factors, including the heating area, which is directly proportional to the length and diameter of the pipes. Most widespread in everyday life we received models with the following characteristics:
- Recommended pipe diameter– from 25 to 160 mm
- Connecting jumpers for sectional models – from 30 mm
- Distance between main pipes – from 50 mm
- Maximum pressure– 10 MPa
- Material– high carbon steel
We make a register with our own hands
Anyone who knows how to work with a welding machine is able to make a heating register on their own. The simple design can be filled with antifreeze or oil.
Introductory video on production
To make a heating device with your own hands, it is recommended to follow the instructions:

In portable structures, it is necessary to install a heating element with a power of 1.5 to 6 W, which will operate from a regular outlet. If the system is running on heating boiler, the efficiency of the registers can be increased by installing a powerful circulation pump.
Main advantages
Among numerous benefits heating registers should be noted:
In custody
Of course, heating registers are replacing classic heating radiators. In private homes they can be found in rooms with more aggressive conditions (toilet, bathroom, periodically unheated premises etc.). For good master It won’t be difficult to make such a device yourself.
DIY heating register
Calculation of parameters and drawing
The first stage of making a heating register with your own hands is design. It is clear that it will not be possible to make a heating register normally by eye. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out a number of additional calculations, based on which it will be possible to select the optimal heat exchanger. When making heating registers, many factors need to be taken into account:
- power;
- design;
- installation methods.
Before you make heating registers with your own hands, you need to understand that this is a heating device, which means it must warm up a certain room. Its heat transfer must correspond to the situation; do not install a heat exchanger covering the entire wall in a small room. One meter should account for from 100 to 200 kilowatts, depending on the region. There is a formula for calculating the heat transfer of heating registers. It includes the following values:
- heat exchanger length in meters;
- internal section in meters;
- metal thermal conductivity coefficient;
- delta of supply and return temperatures;
- number "P".
To determine heat transfer, you need to multiply all the components of the calculation. Of course, from this formula you can separately determine each of the above values. So, knowing the square footage of the room, you can determine what dimensions the structure should have. Often homemade registers for heating are made from scrap materials, so it is not possible to select some parameters. It is necessary to adjust the entire structure to the existing characteristics, while not forgetting about the functionality of the heat exchanger.
When calculating the length of the heat exchanger, you need to remember that the resulting value indicates the total length of the pipes.
For example, according to the formula we got a value of five meters. This means that both one five-meter pipe around the perimeter and several sections, the sum of the lengths of which will be the same five meters, are suitable for heating. The point is to maintain the heat exchange area.
There are two methods for placing main (thick) pipes:
- horizontally;
- vertically.
In principle, there is no difference in manufacturing. If you take a horizontal structure and rotate it 90 degrees clockwise, you get a vertical heat exchanger. This will make a difference when installing on a circuit.

That's the whole difference between vertical and horizontal register
In addition, the heating registers are secured with special jumpers. There may be one or two such jumpers. Also, the connection of horizontal sections can be carried out using couplings of the same diameter, which are welded into the end. These are the so-called serpentine registers. You can choose any method of assembling a heating register from pipes with your own hands, the main thing is that you have enough skills to perform it.
In order not to complicate the register manufacturing process, we will use a scheme for connecting horizontal sections with two pipes. Heating register, drawing:

Heating register drawing
For work we will need:
- three identical pieces of pipe;
- four connecting pipes;
- six plugs.
The distance between the heating register pipes may be larger, but not smaller. Moreover, if pipes of large diameter are used, the distance between them is determined by the formula: diameter x 1.5. This distance is optimal. The next stage is welding.
Assembly individual elements The structure is put together by welding metal. This can be done in any way convenient for you. How to weld a heating register correctly? In fact, it all depends on what kind of welding machine you have:
- electric arc (manual, semi-automatic);
- gas.
The most widely used are electric arc manual welders, since they are the cheapest and simplest. With this device you can connect metal parts, and cut them. On large parts you need to cut holes for the pipes. This should be done near the edge, retreating one diameter of the pipe. There will be four holes on the middle section, two on the first and outer sections.

Holes for connecting pipes
After this, on a flat horizontal surface we lay out all the elements in one structure and make tacks at the base of the pipes. You need to make either two tacks along the equator of the pipe, or three evenly around the entire circumference, as in the Mercedes badge. If the position of the tacks is incorrect, the part may fail during welding. After making sure that the register geometry is correct, you can proceed to welding.
While working in the melting bath, you need to maintain a high temperature and distribute the molten metal. The electrode must constantly move along a certain trajectory. How to weld a heating register, the simplest trajectories of electrode movement:
- left - right (herringbone);
- forward - backward (with influx).
The most important point is the formation of the root of the weld on the tack and the exit from the tack. The process is performed with a gap, since the welder needs to change the position of the electrode. Although, with proper skill, you can cook without interruption. After the seam has cooled, you need to knock off the sludge with a hammer. So, all that remains is to weld the ends with plugs, which must first be cut from metal of the same thickness.
By the way, to produce registers you need to take at least three millimeters of steel.
As a result, we have a blank in which holes for supply and return, as well as an air vent, will be cut in the future. The air vent, the same Mayevsky valve, removes air pockets that reduce the efficiency of the heat exchanger. You can also read more about . Connecting the registers to the heating system is the last stage, after which you can carry out hydraulic check and put equipment into operation.
In addition, this blank can be used to manufacture a register with an electric heating element. A hole for the heating element is cut out at the bottom end, and a expansion tank open type.
Connection diagrams for heating registers
Setting the heating register to cotrur
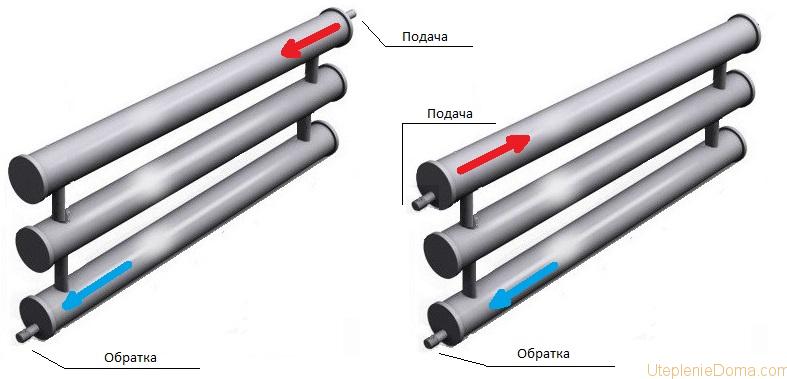
Now that the heat exchanger is ready, you need to install the heating register on the circuit. Just like a normal battery, it can connect different ways, and the flow should always be higher than the return. We wrote about it in one of the previous articles. Installation of pipes to the heating register is carried out:
- at one end;
- at different ends.
The latter connection scheme for heating registers is called diagonal and is more preferable. When we know where the supply and return will be, we can make holes in the ends for threaded couplings. Fittings connecting the heat exchanger to the circuit will then be screwed to these couplings. An air vent is welded on the opposite side of the supply. It can be located at the end, but it is better for the valve to be at the top.
Before installing the heating registers, remember that it is quite heavy, even without coolant, and even more so when filled with water. Therefore, it is necessary to provide reliable fastenings. The heat exchanger can be placed on the floor or hung on the wall. It is better, of course, to make legs and place it on the floor, additionally securing it with fastenings to the wall. Do not forget that there should be about 25 centimeters from the surface of the heat exchanger to the walls and floor.
Another recommendation concerns the location of the heat exchanger. As you may have noticed in apartments, the battery is always under the window. On the one hand, it heats up cold air emanating from the glass, and on the other hand, it warms outer wall. That is, you need to try to install registers along the walls that are in contact with the street.
One of important elements Any heating system, without which its operation is impossible, are heating devices. Today, the market offers a huge range of radiators for every taste and income. And, despite the existing variety of forms and high efficiency modern models, a special place in the lineup similar products occupied by heating registers.
Structurally, such heating devices are parallel smooth-walled pipes with a diameter of at least 32 mm, connected to each other by short transverse jumpers.
I would like to note that the registers were found wide application in times of total shortage, when traditional radiators, not even different high quality, could be purchased with difficulty. However, such devices should not be underestimated: in some cases they can be more effective than many modern heaters and batteries.
In most cases, this type of device is used for heating technical (garages, utility rooms, warehouses, etc.) and industrial buildings. But it is not uncommon to find them in autonomous schemes heating supply of private houses.
Figure 1 – Example of a heating system with registers
Advantages and disadvantages of heating registers
The main advantages of these devices, first of all, should be the simplicity of design (they can be designed and produced with your own hands), increased strength(resistance to changes in pressure and temperature, independence from the quality and type of coolant) and long term trouble-free operation, subject to the quality of installation.
Other advantages should also be noted:
- variability of configurations;
- high degree of heat transfer;
- possibility of heating rooms with large area with relatively compact dimensions of the devices;
- longer cooling (this is explained by the presence of a large volume of coolant in the devices);
- ease of care;
- relatively low price.
Despite the above advantages, comparative effectiveness Heating registers are still inferior to traditional radiators, which is due to the smaller total heat transfer area. But this drawback can be eliminated by modifying the basic design of the devices, for example, by increasing the number of horizontally located elements or by welding additional metal parts to them, for example, vertical plates.
Existing types of heating registers
The entire existing variety of such devices can be classified into three groups.
By design features:
- sectional - made in the form of one or several parallel pipes with plugs at the ends and connected to each other by pipes through which the coolant completely fills the device;
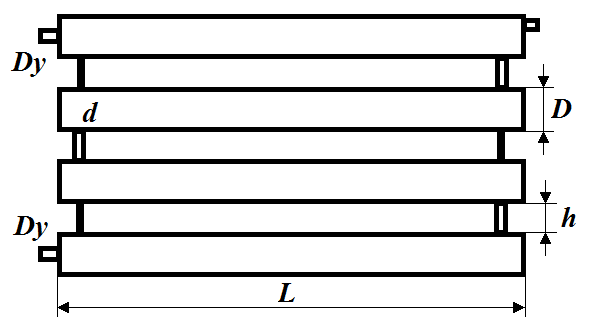
Figure 2 – Sectional register option
- serpentine (S-shaped) - in such models, horizontally located elements are connected to each other through arc-shaped elements of the same diameter, made of the same materials; As a result, such heating registers have solid structure, which leads to greater thermal efficiency due to an increase in the heat transfer area and reliability due to the absence of sections of variable cross-section.

Figure 3 – Option for coil heating register
By type of material:
- cast iron - different high strength, durability, but have a large mass, complicating the installation process; connection of cast iron registers to the heating system is carried out using flanges: one is welded to the pipeline, the second (monolithic) is included in the design of the device;
- aluminum - the demand for this type of device is due to its rather attractive appearance, low weight, good indicator heat transfer; such heating devices there are no welds or connections; the main disadvantage is the high cost;
It is necessary to take into account that aluminum registers are sensitive to the quality of the coolant, therefore, in conditions central heating they should be used with caution.
- steel - the design of such models has enough a large number of welding seams; connection to the heating system is also made by welding; therefore, reliability and long service life will mainly depend on the quality of installation work.
By installation method:
- mobile (mobile) - such devices are similar in principle of operation electric heaters, the main difference is only in the size of the devices; They are usually used for temporary heating of premises in which work is carried out. Finishing work, or construction houses (cars) for workers;
- stationary - such devices are part of the heating system and are installed in buildings on a permanent basis.
Design features of heating registers and possible connection diagrams to pipelines
As noted above, heating registers are made sectional or S-shaped from pipes with a diameter of 32-200 mm. Moreover, the number of elements, their location and shape may vary depending on the required power of the device.
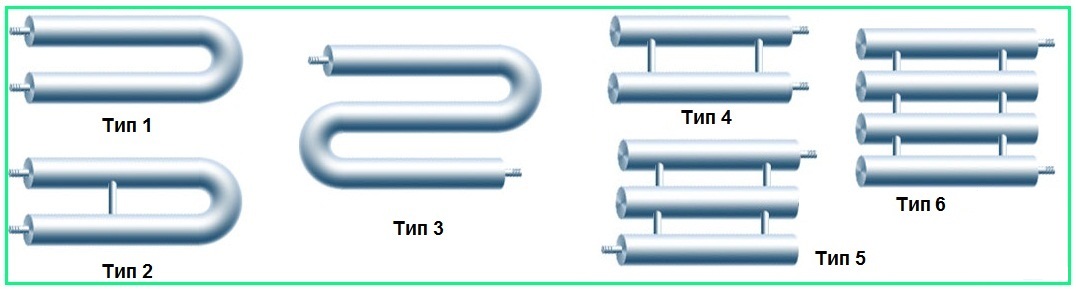
Figure 4 - Sample options design heating registers
To increase the power of registers, one should not strive to use elements of large diameter, because such an approach can lead to loss of boiler performance or the need to purchase more powerful equipment, which is not always advisable.
For the manufacture of such devices, as a rule, smooth-walled pipes are used, but it is also possible to use profile metal. A necessary condition this will take into account the type of material (cast iron, steel), the rules for working with it and compliance with the requirements for welding work.
When making a register with your own hands, it is not recommended to place the elements too close to each other, because this will affect heat transfer. The optimal distance is 50 mm greater than the diameter of the pipes.
Regardless of the design, any model has inlet-outlet pipes for connection to the coolant supply and outlet pipelines, and a fitting for installing an air vent. In sectional devices, mandatory elements are also plugs, which can be elliptical (made to order) or flat, as well as connecting pipes (they are recommended to be placed closer to the ends of the pipes).
Heating registers can be operated in both single-pipe and two-pipe systems. To connect similar devices The following options can be used for heat supply schemes:
- diagonal;
- lateral;

Figure 5 – Diagonal and lateral connection of registers to the heating system
- bottom (this scheme is more appropriate to use when the device is small in size or has a small number of horizontal elements).

Figure 6 – Scheme bottom connection register
Installation of registers in the heating system
First of all, it should be noted that the assembly of such heating devices can be carried out both in the factory and directly on site. In the latter case, the heating registers are supplied as separate elements.
When using models with threaded connections, the process of installing them into the heating system will be no different from installing radiators. If the design of the devices does not provide for threads, welding work will be required.
It should be borne in mind that, unlike radiators, registers should be installed at a slight slope (0.05%) in the direction of coolant movement.
DIY heating registers
Before starting to manufacture heating devices of this type, it is necessary to make an accurate calculation, namely: